1.最大公约数,最小公倍数
1 | int gcd(int x,int y) |
2.快速幂
1 | int qpow(int a,int b,int mod)//a^b |
>>矩阵快速幂 很久以前收集的模板,亲测可用
1 | struct Matrix |
另外一种
1 | struct Matrix |
对元素0较多的矩阵取快速幂时可在Mul函数中加一个小优化:
1 | Matrix Mul(Matrix a,Matrix b) |
3.排列组合
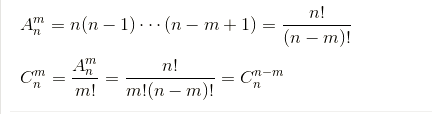
1 | LL A(int n,int m)//n>=m |
组合数性质:从这看到的:https://blog.csdn.net/litble/article/details/75913032
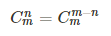
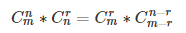
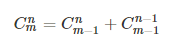
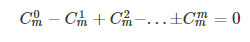
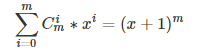
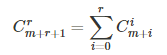

4.错排
D(n) = (n-1) [D(n-2) + D(n-1)](n物品全部错位的方案数)
D(n) = n! [(-1)^2/2! + … + (-1)^(n-1)/(n-1)! + (-1)^n/n!].
记住公式就知道代码了
5.费马小定理: 假如p是质数,且gcd(a,p)=1,那么 a^(p-1)≡1(mod p)。(如果a为整数,p为质数,a和p互质,则a的p-1次幂对p取模永远等于1)